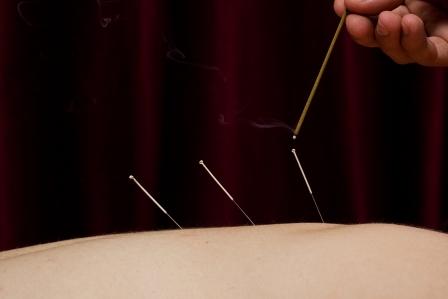
A small case control study carried out in Canada has found evidence that electrodermal activity at acupuncture points (APs) differs between patients with current pain and pain-free controls. Thirty-two patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a typical pain level of at least three (on a 0-10 scale) were compared with 28 case controls who had no medical diagnosis and were pain free. Electrodermal resistance at APs was measured, along with ratings on subjective pain scales. Consistent differences were found between the experimental group and the control group for all pain markers. Similarly, there were significant differences between the groups for electrodermal activity measured at APs along the Bladder, Gall Bladder and Small Intestine channels. The authors conclude that electrodermal resistance at APs can distinguish pain from a no-pain state. (Electrodermal activity at acupuncture points differentiates patients with current pain from pain-free controls. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2013 Mar;38(1):71-80).
Categories: Acupuncture research